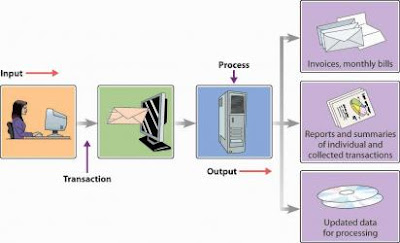
A- TPS: Transaction Processing Systems
Definition: A Transaction Processing System (TPS) is a type of information system that collects, stores, modifies and retrieves the data transactions of an enterprise. A transaction is any event that passes the ACID test in which data is generated or modified before storage in an information system.
Features of Transaction Processing Systems: The success of commercial enterprises depends on the reliable processing of transactions to ensure that customer orders are met on time, and that partners and suppliers are paid and can make payment. The field of transaction processing, therefore, has become a vital part of effective business management, led by such organisations as the Association for Work Process Improvement and the Transaction Processing Performance Council.
Transaction processing systems offer enterprises the means to rapidly process transactions to ensure the smooth flow of data and the progression of processes throughout the enterprise. Typically, a TPS will exhibit the following characteristics:
Rapid Processing: The rapid processing of transactions is vital to the success of any enterprise – now more than ever, in the face of advancing technology and customer demand for immediate action. TPS systems are designed to process transactions virtually instantly to ensure that customer data is available to the processes that require it.
Reliability: Similarly, customers will not tolerate mistakes. TPS systems must be designed to ensure that not only do transactions never slip past the net, but that the systems themselves remain operational permanently. TPS systems are therefore designed to incorporate comprehensive safeguards and disaster recovery systems. These measures keep the failure rate well within tolerance levels.
Standardisation: Transactions must be processed in the same way each time to maximise efficiency. To ensure this, TPS interfaces are designed to acquire identical data for each transaction, regardless of the customer. Controlled Access Since TPS systems can be such a powerful business tool, access must be restricted to only those employees who require their use. Restricted access to the system ensures that employees who lack the skills and ability to control it cannot influence the transaction process.
Definition: Computer system designed to provide assistance in determining and evaluating alternative courses of action. A DSS (1) acquires data from the mass of routine transactions of a firm, (2) analyses it with advanced statistical techniques to extract meaningful information, and (3) narrows down the range of choices by applying rules based on decision theory. Its objective is facilitation of 'what if' analysis and not replacement of a manager's judgment.
They are a class of computerized information system that support decision-making activities. DSS are interactive computer-based systems and subsystems intended to help decision makers use communications technologies, data, documents, knowledge and/or models to complete decision process tasks.
A decision support system may present information graphically and may include an expert system or artificial intelligence (AI). It may be aimed at business executives or some other group of knowledge workers.
Typical information that a decision support application might gather and present would be, (a) Accessing all information assets, including legacy and relational data sources; (b) Comparative data figures; (c) Projected figures based on new data or assumptions; (d) Consequences of different decision alternatives, given past experience in a specific context.
There are a number of Decision Support Systems.
A decision support system may present information graphically and may include an expert system or artificial intelligence (AI). It may be aimed at business executives or some other group of knowledge workers.
Typical information that a decision support application might gather and present would be, (a) Accessing all information assets, including legacy and relational data sources; (b) Comparative data figures; (c) Projected figures based on new data or assumptions; (d) Consequences of different decision alternatives, given past experience in a specific context.
There are a number of Decision Support Systems.
These can be categorized into five types:
Communication-driven DSS Most communications-driven DSSs are targetted at internal teams, including partners. Its purpose are to help conduct a meeting, or for users to collaborate. The most common technology used to deploy the DSS is a web or client server.
Communication-driven DSS Most communications-driven DSSs are targetted at internal teams, including partners. Its purpose are to help conduct a meeting, or for users to collaborate. The most common technology used to deploy the DSS is a web or client server.
Examples: chats and instant messaging softwares, online collaboration and net-meeting systems.
Data-driven DSS: Most data-driven DSSs are targeted at managers, staff and also product/service suppliers. It is used to query a database or data warehouse to seek specific answers for specific purposes. It is deployed via a main frame system, client/server link, or via the web. Examples: computer-based databases that have a query system to check (including the incorporation of data to add value to existing databases.
Document-driven DSS: Document-driven DSSs are more common, targeted at a broad base of user groups. The purpose of such a DSS is to search web pages and find documents on a specific set of keywords or search terms. The usual technology used to set up such DSSs are via the web or a client/server system.
Knowledge-driven DSS: Knowledge-driven DSSs or 'knowledgebase' are they are known, are a catch-all category covering a broad range of systems covering users within the organization seting it up, but may also include others interacting with the organization - for example, consumers of a business. It is essentially used to provide management advice or to choose products/services. The typical deployment technology used to set up such systems could be slient/server systems, the web, or software runnung on stand-alone PCs.
Model-driven DSS: Model-driven DSSs are complex systems that help analyse decisions or choose between different options. These are used by managers and staff members of a business, or people who interact with the organization, for a number of purposes depending on how the model is set up - scheduling, decision analyses etc. These DSSs can be deployed via software/hardware in stand-alone PCs, client/server systems, or the web.
Data-driven DSS: Most data-driven DSSs are targeted at managers, staff and also product/service suppliers. It is used to query a database or data warehouse to seek specific answers for specific purposes. It is deployed via a main frame system, client/server link, or via the web. Examples: computer-based databases that have a query system to check (including the incorporation of data to add value to existing databases.
Document-driven DSS: Document-driven DSSs are more common, targeted at a broad base of user groups. The purpose of such a DSS is to search web pages and find documents on a specific set of keywords or search terms. The usual technology used to set up such DSSs are via the web or a client/server system.
Knowledge-driven DSS: Knowledge-driven DSSs or 'knowledgebase' are they are known, are a catch-all category covering a broad range of systems covering users within the organization seting it up, but may also include others interacting with the organization - for example, consumers of a business. It is essentially used to provide management advice or to choose products/services. The typical deployment technology used to set up such systems could be slient/server systems, the web, or software runnung on stand-alone PCs.
Model-driven DSS: Model-driven DSSs are complex systems that help analyse decisions or choose between different options. These are used by managers and staff members of a business, or people who interact with the organization, for a number of purposes depending on how the model is set up - scheduling, decision analyses etc. These DSSs can be deployed via software/hardware in stand-alone PCs, client/server systems, or the web.

The information is helpful!thank you
ReplyDelete